What is DCP?
peroxide used as a crosslinking agent in the polymer industry for natural and synthetic rubbers. DCP has a melting temperature of 40°C and a thermal decomposition starting at 70°C. It finds applications in the rubber and plastic industries.
Home / DCP
Dicumyl Peroxide (DCP)
Dicumyl Peroxide or “bis (1-methyl-1-phenylethyl) peroxide” is a chemical substance with an aromatic structure. DCP is one of the most widely used types of peroxide in the polymer industry as a crosslinking agent (creating crosslinks) for natural and synthetic rubbers.
Properties of Dicumyl Peroxide
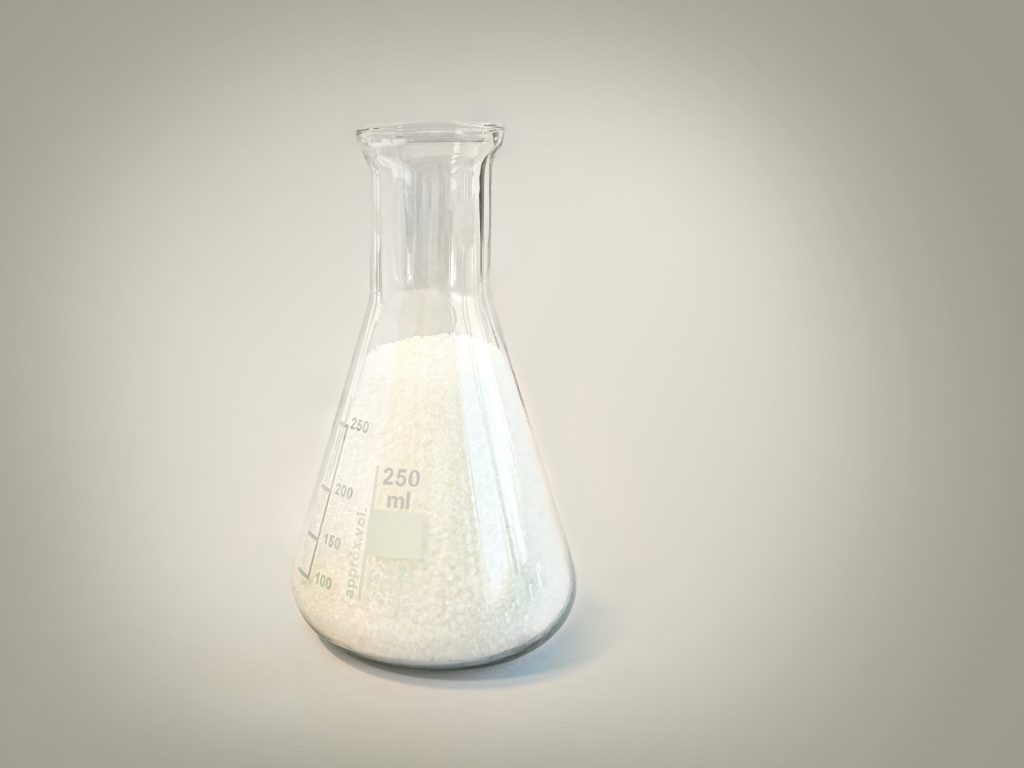
DCP is a yellowish-white powder that appears in crystal form. It has low solubility in water (0.4-2 mg/l) but is highly soluble in alcohols, esters, and aromatic hydrocarbons. The melting temperature of Dicumyl peroxide is about 40°C, and its thermal decomposition temperature is 70°C. Therefore, it is recommended to store DCP below 39°C, with the best storage temperature being 4°C. It is important to note that DCP is highly flammable and should be kept away from any flammable materials. Moreover, it strongly reacts with substances such as acids, bases, reducing elements, and heavy metals, which may lead to combustion or explosion.

The half-life of DCP
The half-life of this substance is 10 hours at 120°C, 1 hour at 140°C, and 1 minute at 185°C. Half-life means that half of the peroxides decompose into radical structures in 10 hours at 120 degrees Celsius.
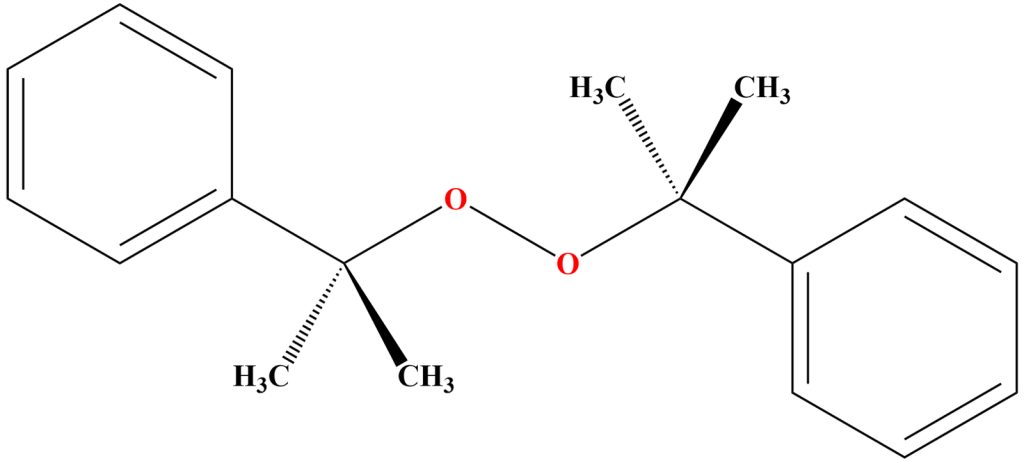
Chemical Structure of DCP
The structure of dicumyl peroxide contains two oxygens that are bound to each other by a covalent bond. The organic groups in the DCP peroxide structure include two phenylethyl groups and two methyl groups. The chemical formulation of DCP is (C₆H₅CMe₂O)₂.
Technical Specification of DCP
Chemical formula | (C6H5C(CH3)2O)2 |
Molecular weight | 270.37 g/mol |
Boiling point | Decomposes below the boiling point |
Decomposition temperature | Start at 70 °C |
Flash point (closed cup) | 110 °C |
Density | 1.56 g/cm3 (25 °C) |
Vapor pressure | <0.1 hPa (at 60 °C) |
Applications of Dicumyl Peroxide
Dicumyl peroxide (DCP) is a high-temperature catalyst widely used in the rubber and plastic industries. It is a potent oxidizing agent that is used for bleaching and deodorizing textiles and papers. DCP is frequently employed as a cross-linking agent for materials such as polyethylene (PE), ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymer, and ethylene-propylene terpolymer (EPT). It is also used as a curing agent for unsaturated polystyrene (PS). Moreover, DCP is applied to various resins to improve their physical properties, which makes it a popular choice in the manufacturing of architectural materials, decorations, electronics, electric insulators, plastic foams, composite parts, footwear, and many other products.
Vulcanization of Rubbers by Dicumyl Peroxide (DCP)
Dicumyl peroxide is a commonly used cross-linking agent for peroxide vulcanization of rubber compounds. It is a white crystalline substance that has good processing and thermal stability. Moreover, it is easy to use and safe to handle. The curing process for rubber compounds treated with dicumyl peroxide typically takes place within the temperature range of 160°C – 190°C.
We are here to guide you and provide advice
